Advantages and Disadvantages of MBBR Wastewater Treatment
By: Tom Frankel
Post Date: noviembre 21st 2019
Table Of Contents
- WHAT IS MBBR WASTEWATER TREATMENT?
- HOW DOES MBBR WASTEWATER TREATMENT WORK?
- ADVANTAGES OF MBBR WASTEWATER TREATMENT
- DISADVANTAGES OF MBBR WASTEWATER TREATMENT
- INDUSTRIES THAT WOULD BENEFIT FROM MBBR WASTEWATER TREATMENT
A wide variety of industries must treat the wastewater they produce so it can be recycled or released into natural bodies of water. The challenge for these industries is in finding wastewater treatment processes that are efficient and effective. Moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) is an innovative wastewater treatment process that any company needing wastewater purification should consider.
This process saves space, is easy to operate, is low-maintenance, can effectively resist shock loads and works efficiently to treat wastewater quickly. Moreover, it is a natural biological process. This article covers MBBR in more detail, explaining its advantages as well as some potential disadvantages to consider.
What Is MBBR Wastewater Treatment?
A moving bed biofilm reactor is a biological wastewater treatment process, meaning it is a natural process that uses biofilm to remove waste from wastewater. Microorganisms attached to media in the water consume unwanted waste, leaving water cleaner.
This technology emerged in the late 1980s in Norway and has since become a popular means of wastewater treatment due to some significant benefits it offers. This process provides a safe and environmentally sustainable means of removing organic substances, measured in terms of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), as well as achieving nitrification and denitrification.
MBBR can function as a standalone process, but it is often part of a more comprehensive regimen for wastewater treatment. It is typically not the first nor the last method of treatment for wastewater but performs a vital function as part of a multi-step method for purification. This is why many MBBR process flow diagrams you’ll find include other steps, such as grit removal or disinfection in addition to the MBBR aeration tank.
How Does MBBR Wastewater Treatment Work?
In MBBR wastewater treatment, a reactor, or basin, is filled with water and thousands of small plastic pieces, known as carriers or media. These media look like hexagonal wheels and are specially designed to provide the perfect surface for waste-consuming microorganisms to thrive. These pieces form a biofilm that provides the solution for removing waste in the water.
The plastic material these carriers are made out of has a density similar to that of water, which allows the media to be evenly suspended throughout the water. Additionally, at the bottom of the reactor, an aeration grid causes the media to remain active throughout the wastewater so they can come into contact with all of the waste in the water. As these pieces flow through the wastewater, the microorganisms living on the media consume the waste in the water. A sieve keeps the media from escaping through the exit of the tank.
Advantages of MBBR Biological Treatment of Wastewater
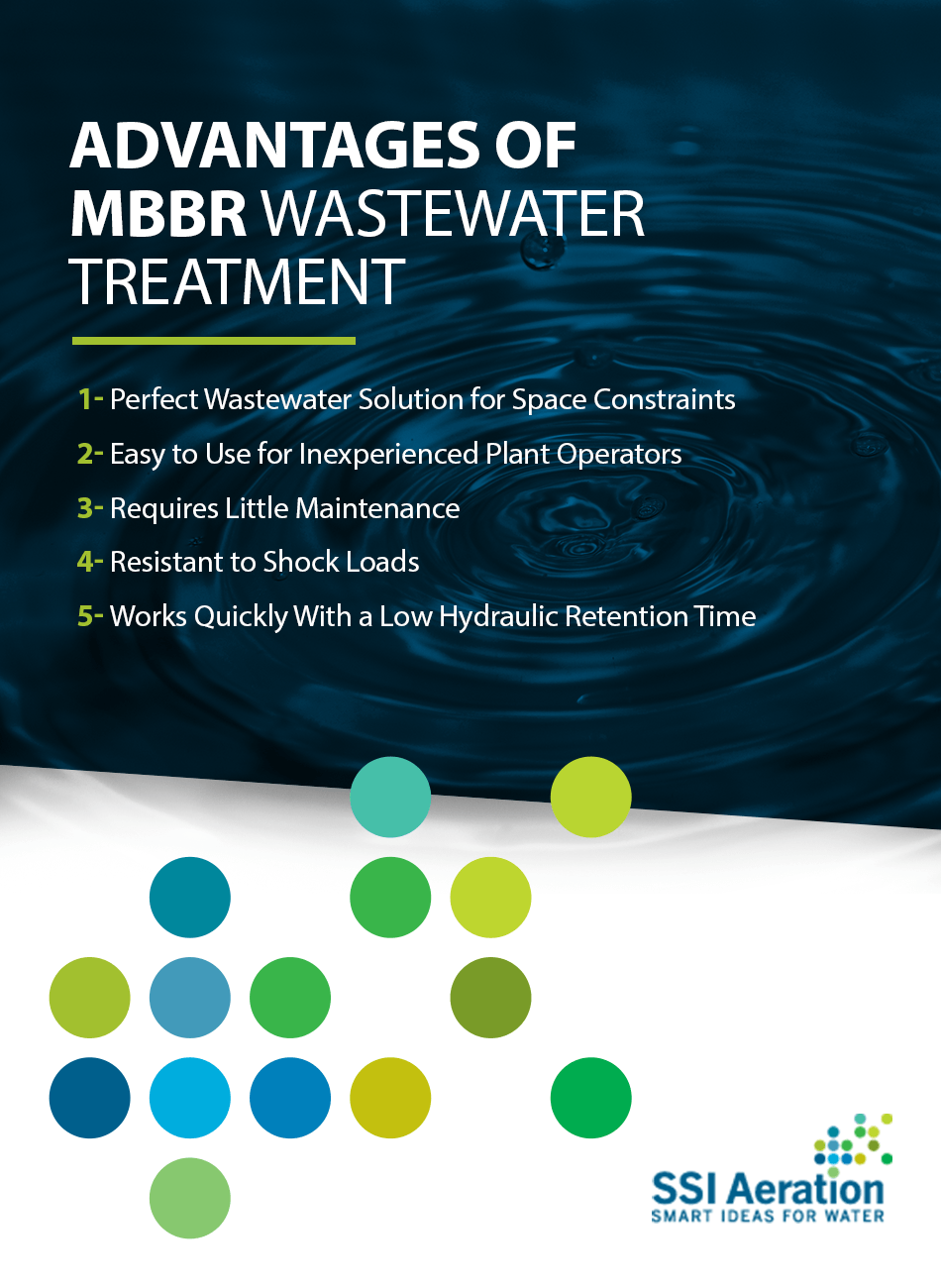
There are several key benefits of an MBBR wastewater treatment system. These advantages make a biofilm reactor process the best choice for some facilities over traditional processes such as membrane bioreactor or activated sludge. Considering the pros and cons of MBBR wastewater treatment can help companies determine whether this option is the best fit for their facility.
1. Perfect Wastewater Solution for Space Constraints
One major advantage of MBBR is that this process doesn’t require a lot of physical space. In fact, MBBR is known for its small footprint compared to other biological water treatment methods. The same volume of wastewater flow can be treated by an MBBR tank a fraction of the size of a tank used for a trickling filter or activated sludge process.
The small footprint of the MBBR process is a major advantage for industrial facilities that are dealing with space constraints. When wastewater treatment systems take up a significant amount of space, that could mean less space for other machinery and systems that are vital to your operations. An MBBR aeration tank can free up space in your facility while providing the same effective treatment as biological processes that demand three times the amount of space.
If a facility needs to add to the systems it already has to treat a higher volume of wastewater, MBBR tanks are an excellent option to consider since they can easily be added to the existing system without taking up a great deal of space. Existing tanks can also be retrofitted for use as an MBBR aeration tank.
2. Easy to Use for Inexperienced Plant Operators
Another one of the advantages of biofilm reactors is that they are easy to operate. The science behind this process may be somewhat complex, but the process itself is straightforward.
Companies that produce wastewater need to determine several factors to calculate the most effective design for their MBBR system. These factors include the surface area loading rate (SALR) along with wastewater flow rate and nitrate, ammonia or BOD concentration. These factors can help determine the necessary carrier surface area and tank volume for a successful MBBR process. Calculations differ depending on whether the goal is single- or two-stage BOD removal, single-stage nitrification, two-stage BOD removal and nitrification, post-anoxic denitrification or pre-anoxic denitrification.
Once the correct design has been determined, operating the system is quite easy. Because the system is flexible and can respond to changes easily on its own, the operator rarely needs to make adjustments. Nature takes its course, and the system automatically produces effluent with reduced or eradicated waste pollutants.
Another of the MBBR advantages that can make MBBR a preferable option for many industrial facilities is that they require little maintenance. Whereas other systems tend to require maintenance actions to keep the system operating, MBBR systems tend to function efficiently and effectively on their own with little intervention.
For example, when the system remains in continual operation, there is no need for return sludge flows or backwashing. Because the aeration grid keeps the media moving around in the tank, clogs are not an issue. Because the system self-moderates to provide the optimum amount of productive biofilm, operators don’t need to take any action to maintain the correct food to microorganism ratio (F/M).
The maintenance that is typically required for an MBBR system consists of monitoring and operating pumps and blowers, as well as performing routine maintenance on screening, clarifier, influent equalization, integrated control and sludge handling systems.
4. Resistant to Shock Loads

Another advantage MBBR systems offer is that they are flexible and can adjust to varying loads. This means they can resist shock loads effectively. Because MBBR systems draw on the benefits of both fixed film and suspended growth biological processes, the MBBR process can handle high organic loads without being undone by a shock load or another drastic change, such as atemporary spike in pH levels.
A 2014 study by Nakhli et al. tested the capabilities and limitations of an aerobic moving bed biofilm reactor and found that the reactor effectively resisted shock loading — remaining highly stable in the face of organic, hydraulic and salt shock loadings — and recovered from these shock loads relatively quickly. This result confirmed the findings of earlier studies, which also demonstrated MBBR systems’ unique ability to resist shock loading.
The researchers suggest that it may be the system’s high concentration of biomass which contains gradually acclimated active microbial consortia along with the sheer amount of surface area present among the many carriers in the reactor that allow MBBR systems to handle shock loading so effectively.
5. Works Quickly With a Low Hydraulic Retention Time
Hydraulic retention time (HRT) is the measure of how much time a water treatment system takes to effectively treat the influent. For some systems, this can be a long time, which means the process moves slowly. The slower the process, the less wastewater can be treated in a given amount of time.
When it comes to MBBR systems, their design equips them to work quickly, achieving a relatively low HRT. In most cases, the HRT for MBBR systems is just a few hours or less. The constantly moving media and the high concentration of biofilm make this low HRT possible.
Because MBBR systems work so quickly, a plant can process more wastewater during a day using an MBBR system as they could another type of system with the same capacity. Revisiting the point about an MBBR’s smaller footprint, this means that a smaller system can treat more water on a faster timeline than equivalent systems. This makes MBBR systems an exceptionally efficient choice.
Disadvantages of MBBR Wastewater Treatment
As with any possible solution, MBBR also involves some disadvantages. The disadvantages of an MBBR system include:
- Manual monitoring: One disadvantage that applies to MBBR systems also applies to biological water treatment processes in general. Whereas other types of water treatment can use sensors to keep track of the system’s progress, with a biological system such as an MBBR tank, an operator must take samples periodically and analyze them to ensure the bacteria on the carriers is still thriving.
- Skilled experts: This leads to another disadvantage of biological systems — operators must be skilled experts in the field of biological water treatment. This is necessary so they can properly analyze the media to ensure it’s still doing its job of decomposing the waste in the tank. Of course, as we’ve seen, operating the tank itself is a simple, mostly hands-off job.
- Insects: Another disadvantage of biofilms that can come from working with biofilm is that some insects, like sewage flies, mosquitoes and red worms, will be attracted to it. This can mean you lose part of the biofilm on the carriers to insects consuming it, thereby compromising the effectiveness of the system. Treatment plants can hedge against this problem by using tanks designed to keep these insects out.
- Escaping carriers: Even without insects present, some users have complained that the carriers can wash out of the system over time, despite the strainers in place to keep them in. This can also be attributed to a possible design flaw with the tank itself. With a properly designed system, there are far more advantages than there are disadvantages to using an MBBR system.
Industries That Would Benefit From MBBR Wastewater Treatment

Any industry that must treat or recycle the wastewater it produces can benefit from an MBBR system. Let’s take a look at several industries that can use an MBBR to effectively treat the wastewater they produce:
- Textile industry: The textile industry produces wastewater that contains dyes, thickeners, wetting agents and other pollutants that must be removed before water can be reused. Typically, the best method for textile mills is to start with a chemical pre-treatment, such as advanced oxidation process, and then move to a biological treatment stage. Research has proven MBBR to be an effective option for biological treatment of textile wastewater.
- Chemicals manufacturing: Manufacturers that produce pesticides, plastics or other chemicals must treat their wastewater before reusing or disposing of it since it contains harmful organic compounds. MBBR can provide an effective means for lowering the BOD of influent enough for the water to be considered safe.
- Food and beverage industry: The food and beverage industry produces a great deal of wastewater from a number of processes, including washing ingredients, for example. The wastewater food and beverage manufacturers produce tends to be non-toxic, but it has high concentrations of suspended solids and BOD. MBBR is an effective choice for removing organic matter to lower BOD levels.
- Municipal sewage plants: For some industries, treating wastewater isn’t just a small part of what they do — it’s their main function. This is the case for municipal sewage plants that deal with water which contains large amounts of organic matter that must be removed before the water can reenter the system. MBBR systems can play a valuable part in a comprehensive system for wastewater treatment at sewage plants.
Finding the Best MBBR System for Your Application
A well-designed MBBR system can save a company space, money and time, all while providing exceptionally effective water treatment capabilities. With MBBR process design services from SSI Aeration, Inc., wastewater treatment plants can arrive at solutions that improve their current systems and improve their overall efficiency.
For the best MBBR technology has to offer, consider the EEVolved MBBR from SSI Aeration, Inc. An advanced knowledge of hydrodynamics, biofilm and aeration integration went into the design of the EEVolved MBBR. This system can be customized to fit the needs of any wastewater treatment facility. The cost of this cutting-edge system depends on factors such as the scope and specifications of your company’s project.
To learn more about what this system might look like for your facility, request an MMBR system quote today. You can also contact a representative who would be happy to answer your questions concerning MBBR and other wastewater treatment methods. As a global leader in wastewater treatment technologies with well over two decades of experience in the field, SSI Aeration, Inc. is a company you can trust for the very best in modern wastewater treatment plant equipment.

Mr. Frankel co-founded SSI in 1995 with experience in design and distribution of engineered systems. He is in charge of sales, marketing and operations in the company. Mr. Frankel holds multiple US patents related to diffusers. He is a graduate of Washington University in St. Louis.


